Governance refers to Data Governance in MDM.
Governance describes the act of managing data access (i.e. who accesses certain data sets based on role, application, etc.).
| Governance... | |
|---|---|
| references | where the Master Data is stored |
| provides | visibility to data between zones and adaptors |
| contains |
|
ACLs are a key component of YOUnite and are different from permissions in that they control where data flows through the system. Permissions control who can manage zones, users, groups, permissions, and roles.
An ACL chain can be thought of as a series (chain) of policies (ACLs) that can be applied to a data event that occurs in the MDM ecosystem.
An access control list, or ACL, is a list of properties that when combined, create a policy that controls data flow between zones and adaptors. The list of ACL properties includes:
Data events in YOUnite parallel the HTTP requests GET, PUT, POST and DELETE.
Not all ACL types use all of the ACL properties.
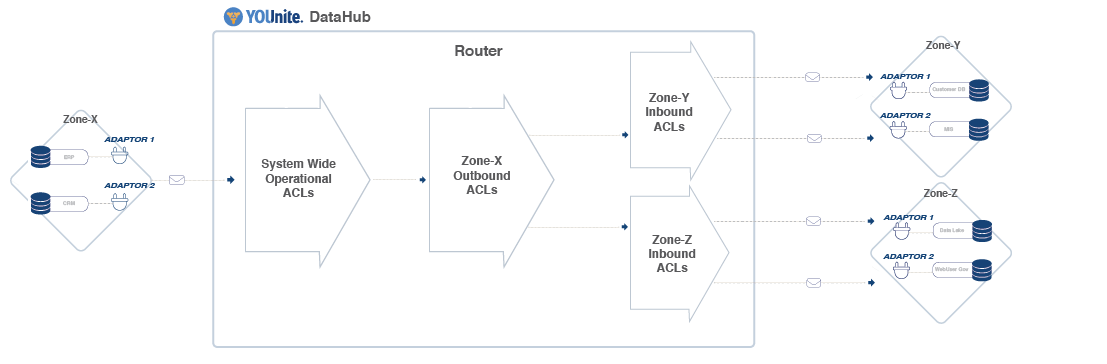
ACLs are linked together to form ACL chains. They behave similar to network firewall chains but apply to an organizations data entities linked to YOUnite. When a data event occurs to a source entity, the change is transmitted to the YOUnite Router and the appropriate ACL chains are consulted and data is propagated (allowed) or restricted based on the ACLs in the ACL chains. Care must be taken to order the ACLs on a chain properly since the first ACL match is applied to a data event.
There are three types of ACLs:
Each zone has both an inbound and outbound ACL chain which are controlled by the zone data steward.
Operational ACLs control which zones can create or delete a federated data record for a specific domain version. Operational ACLs are controlled by the Data Governance Steward.
Outbound ACLs can be thought of as policies on out-bound data. By default, all ACLs are open. Outbound ACLs are the controls a Source Zone's data steward sets on Destination Zones:
| Operation | Data Event Description |
|---|---|
| PUT | When the source zone allows or restricts the changes that occur inside the source zone from flowing outbound to destination zones. |
| POST | When the source zone allows or restricts new data that is created on adaptors in the source zone from flowing outbound to destination zones. |
DELETE | When the source zone allows or restricts "deletes" that occur inside the source zone from flowing outbound to destination zones. |
| GET | What destination zones are allowed or restricted from using the source zone's data when assembling data. |
Polices can be set on the following:
| Entity | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| Source Adaptor | The adaptor in the source zone where the data event originates. | ALL |
| Destination Zone | The destination zone where the data event can be delivered (i.e. it has adaptors that are capable of handling the event) | ALL |
| Adaptor | An adaptor in the destination zone capable of handling the data event. | ALL |
| Domain Version | The data associated with a data event will contain data that belongs to one or more domain versions. | ALL |
| DR | One or more federated data records that belong to the Domain Version | ALL |
| Domain Version | Data events contain a federated data records that belong to one or more Domain Versions. | ALL |
| Domain Version Property | The union of all instances of a specific domain property stored on adaptors inside of the Source zone (unless constrained to a subset of adaptors) | ALL |
| Allow GET / Restrict GET | Allow or restrict GET data events. | neither is set |
| Allow PUT / Restrict PUT | Allow or restrict PUT data events. | neither is set |
| Allow POST / Restrict POST | Allow or restrict POST data events. | neither is set |
| Allow DELETE / Restrict DELETE | Allow or restrict DELETE data events. | neither is set |
Inbound ACLs can be thought of as policies on in-bound data. By default, all ACLs are open. Inbound ACLs are the controls a Destination Zone sets on Incoming data requests from Source Zones:
| Operation | Data Event Description |
|---|---|
| PUT | When the destination zone allows or restricts changes that occur in source zones/adaptors from flowing into the destination zone. |
| POST | When the destination zone allows or restricts new data that is created in source zones from flowing into the destination zone. |
| DELETE | When the destination zone allows or restricts deletes that occur in source zone/adaptors from flowing into the destination zone. |
| GET | What source zone/adaptors are allowed or restricted (ignored) by the destination zone when assembling data. |
Policies can be set on the following - the zone data steward in the destination zone, creates the ACL on behalf of the destination zone:
| Entity | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| Source Zone | The originating source zone. | ALL |
| Source Adaptor | The originating source zone's adaptor(s). | ALL |
| Destination Adaptor | The data associated with a data event will contain data that belongs to one or more domain versions. | ALL |
| Domain Version | The union of all data stored on adaptors (unless constrained to a subset of adaptors) inside the zource zone that maps to a given data domain. | ALL |
| Domain Version Property | The union of all instances of a specific domain property stored on adaptors inside of the Source zone (unless constrained to a subset of adaptors) | ALL |
| DR | One or more federated data records that belong to the Domain Version. | ALL |
| Allow GET / Restrict GET | Allow or restrict GET data events. | neither is set |
| Allow PUT / Restrict PUT | Allow or restrict PUT data events. | neither is set |
| Allow POST / Restrict POST | Allow or restrict POST data events. | neither is set |
| Allow DELETE / Restrict DELETE | Allow or restrict DELETE data events. | neither is set |
Operation ACLs are not part of zone data governance. Operational ACLs set policies that set forth for a given data domain version:
There is a single system-wide chain for Operational ACLs that is controlled by the DGS. By default all zones and adaptors can POST and DELETE data records but POST and DELETE polices for data records can be controlled by the DGS.
Operational ACL policies can be on the following:
| Entity | Description |
|---|---|
| Domain Version | The domain version an operational ACL applies to. |
Source Zone | The zone that is allowed to or, restricted from POSTing a data record (DR). |
| Source Adaptor | The adaptor that is allowed to or, restricted from POSTing a data record (DR). |
| Allow POST / Restrict POST | Allow or restrict the source zone or adaptor from creating a data record for the given domain version. |
| Allow DELETE / Restrict DELETE | Allow or restrict the source zone or adaptor from deleting a data record for the given domain version. |
A very simple example it illustrate this point:
| Source Zone | Destination Zone | Destination Adaptor | Domain Version | Policy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zone-X | Zone-Y | ALL | ALL | ALLOW ALL |
| 2 | Zone-X | ALL | ALL | ALL | RESTRICT ALL |
ALL = GET, PUT, POST, DELETE
Following is more involved example using the zones and adaptors from above. ACLs are evaluated from first to last, the first match is applied to an incoming data event:
| Source Zone | Source Adaptor | Destination Zone | Destination Adaptor | Domain Version | Data Records | Policy | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zone-X | ALL | Zone-Y | ALL | ALL | ALL | RESTRICT ALL | Restricts all outbound data events to Zone-Y |
| 2 | Zone-X | ALL | Zone-Y | Adaptor1 | ALL | ALL | RESTRICT ALL | This ACL is useless since ACL #1 already restrict all events to Zone-Y |
| 3 | Zone-X | ALL | Zone-Z | ALL | Customer v1 | DR-123, DR-456 | RESTRICT ALL | Restricts the data records (DR-123 and DR-456) from going to Zone-Z. |
| 4 | Zone-X | Adaptor2 | ALL | ALL | ALL | ALL | RESTRICT ALL | Restricts data events from flowing out of Zone-X's adaptor2 to all zones. |
| 5 | Zone-X | ALL | ALL | ALL | Customer v1 | Customer.ssn | RESTRICT ALL | Restricts a customer's SSN from flowing out of of Zone-X. |
| 6 | Zone-X | ALL | ALL | ALL | ALL | ALL | ALLOW ALL | Allow everything else out i.e. if a data event can be delivered to many adaptors in the YOUnite ecosystem it will be delivered to all adaptors except for the restrictions placed by the above ACLs. ALLOW ALL is the default so in reality, this ACL is unnecessary. |
ALL = GET, PUT, POST, DELETE
After applying all of the above, the end result is:
The image below represents the components involved as a data event is detected at an adaptor and flows through the YOUnite ecosystem.
