Master data management (MDM ) is an approach to reducing data redundancy by maintaining a definitive "record of truth," or Master Data, for critical data in order to supply a single source as a reference. Ideally, MDM organizes data sharing among multiple applications or departments.
It Starts with Data Integration
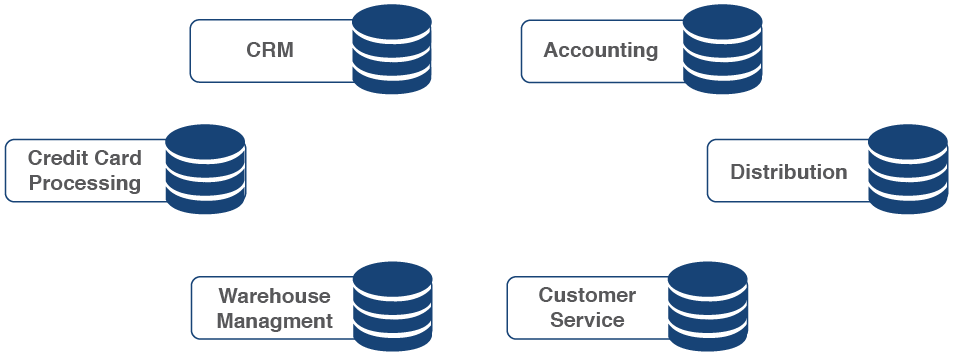
It's common for organizations to have duplicate information on different systems. For example, customer information could be stored in both a CRM and accounting system:
...
For example, imagine a delivery service that stores information about its customers in several systems:
Delivery Service Example
As customer information changes over time (i.e. customer addresses or phone numbers), keeping all the systems up to date becomes exponentially more difficult.
...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
In Master Data ManagementMDM, the set of fields or properties (e.g. name, address, phone number) that define a set of data (e.g. Customer) is called a data domain.
Migrating to
...
MDM
MDM solves the problem of keeping interrelated systems up to date by creating a separate system where data domains (or domains) are defined for all systems inside the organization. The domains provide neutral data formats or schemas for all systems, facilitating data sharing.
...
Implementing MDM involves a process of determining where the data records are stored (whether it's the MDM Data Store or Federated MDM) and managing who (a person or a system) has read, write, update, and delete privileges to those systems.
Data Records vs Master Data
Where data records are the latest, most recent version of a record stored in many systems connected to YOUnite, master data is data in a particular domain or a particular element that has been declared the Record of Truth. It's not always necessary or appropriate for systems to access an organization's master data. Many data access requests are for data records that may or may not contain master data. However, YOUnite has the ability to propagate changes from a system that contains data records to others in the YOUnite ecosystem on a permission-appropriate basis (i.e. governance).
Reviewing New Terms
Several terms have been introduced and it may be helpful to review them before moving on:
- Access Control Lists (ACLs) Data controls that control inbound/outbound messages for any given system, application, or role.
- Adaptor Software located within a system that shares data through the YOUnite Data Hub and acts as the connection point between a system and the YOUniteData Hub. It focuses on ETL (Extract, Transform, and Load) functions, ensuring the outbound data from a system meets the YOUnite Data Hub format requirements, transforming inbound data from the hub into what other systems require.
- Data Domain (Domain) A domain refers to a data entity such as student, course, or customer, etc. and is defined by the parties responsible for data governance. It is a set of fields or properties that define a set of data (i.e. a domain may be a "Student" that includes data (properties) such as student name, address, etc.).
- Data Governance Managing data access (i.e. who accesses certain data sets based on role, application, etc. defining where the Master Data is stored).
- Data Integration (DI) The process of keeping data up to date between disparate systems.
- Data Record The latest (most recent) version of a given record. More technically, JSON objects in motion that follow the data domain model schema of the MDM ecosystem.
- Federated MDM An MDM model in which the data handled through MDM is not stored centrally in the Data Hub but instead a reference to the data is stored that points to the the source system where the data hub can retrieve the data.
- Master Data (MD) The master or golden version of a record (for a customer, for example). The "record of truth" as declared by a Data Governance Steward (DGS) or Zone Data Steward (ZDS).
- Master Data Management (MDM) An approach to reducing data redundancy across systems by maintaining a master file for critical data. MDM is the process of describing and cataloging data inside of an organization and understanding which stakeholders value which sources of data.
- YOUnite Data Store/MDM Data Store A centralized store natively connected to the YOUnite Data Hub that holds data records. The domains configured for this data store are locked in as the source of master data for that domain in the Tenant.
- YOUnite Data Hub The scaleable web application that handles the API and message broker requests through which adaptors and the YOUnite API consumers communicate.
Further Reading
An good source for more MDM background is Mark Allen and Cervo Dalton's Multi-domain Master Data Management: Advanced MDM and Data Governance in Practice. Waltham, MA: Morgan Kaufmann, 2015. (ISBM 978-0-12-800835-5).
Next
...